What is DNA replication? How does it happen? When does DNA replication occur? These questions have intrigued microbiologists for many years. In this blog post, we will briefly introduce the process and attempt to answer some questions about DNA replication.
Learn in This Article
- What Is DNA Replication
- Why Does DNA Replicate
- Why Do We Need to Understand DNA Replication
- When Does DNA Replication Occur
- Where Does DNA Replication Take Place
- How Does DNA Replicate
What Is DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical replicas. The replicas are then used to create new cells, ensuring each cell has a complete set of chromosomes.
DNA replication begins with the unwinding of the double helix and the separation of the two strands. Each strand serves as a template for the DNA replication enzyme polymerase for synthesizing a new complementary strand.
DNA replication is highly accurate. Studies on DNA show that errors occur only about one in every billion nucleotides. This high fidelity ensures that cells maintain their genetic information over many generations.
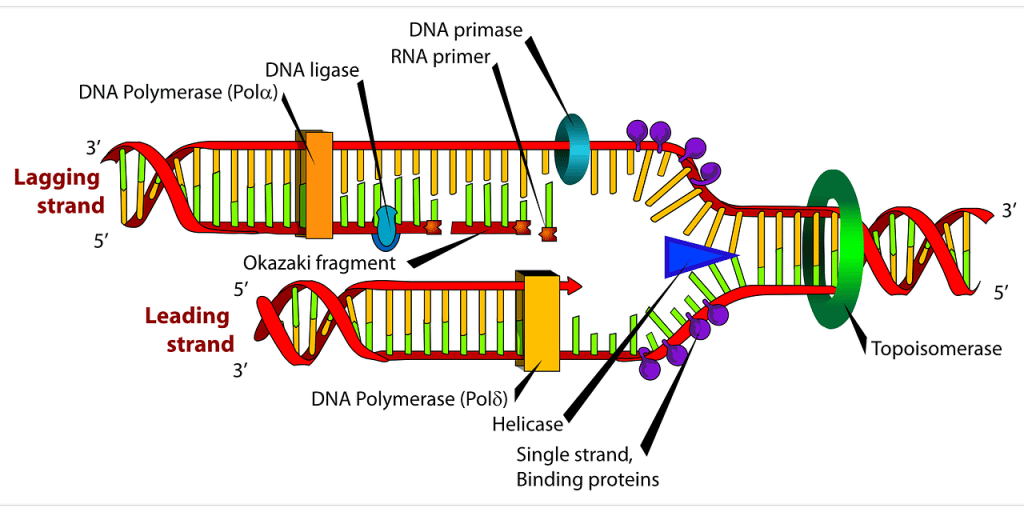
Why Does DNA Replicate
DNA replicates to create more cells. This is important because cells die, and new ones must be created to keep the body functioning. DNA replication is continuous throughout a cell’s lifetime and is essential for maintaining genetic stability.
Why Do We Need to Understand DNA Replication?
Apart from knowing more about cell division, understanding DNA replication and the enzymes are crucial to the advancements in biotechnology and genetic engineering.
When Does DNA Replication Occur
The DNA replication process occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle. This complex process begins when the double helix unwinds and separates into two single strands.
What Triggers DNA Replication
DNA replication is initiated when an initiator protein recognizes a specific DNA sequence within the origin of replication and unwinds a portion of the double helix.
An enzyme called helicase attaches to and breaks apart the hydrogen bonds that hold the bases of the strand together, creating a replication fork. As the helicase moves along the DNA molecule, it breaks these hydrogen bonds and separates the two polynucleotide chains, thus making the template strands the DNA polymerase needs to create new DNA strands.
Where Does DNA Replication Take Place
DNA replication occurs inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, where the chromosomes are stored and where the enzyme machinery required for replication is located.
For prokaryotic cells, the DNA replication location is in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid.
How Does DNA Replicate
DNA replication is a process by which cells copy their genetic information. The first step is the unwinding of the double helix, which is accomplished by enzymes called helicases. The single strands of DNA are then copied by enzymes called polymerases. Then, the two newly formed double helices are joined together by enzymes called ligases.
This process occurs every time a cell is divided, ensuring that each new cell has an identical copy of the original DNA.
Key Takeaways
- DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two exact replicas in preparation for cell division.
- The process of replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle.
- Replication is initiated when an initiator protein recognizes a specific DNA sequence within the origin of replication and unwinds a portion of the double helix.
The location of DNA replication is inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid for prokaryotes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the result of DNA replication?
The result of DNA replication is two identical copies of the original DNA molecule. These copies are then used to create new cells, ensuring that each cell has the same genetic information as the original cell.
Does DNA replication occur all the time?
DNA replication is a continuous process, happening all the time in our cells during cell division to ensure each daughter cell has identical chromosomes. The replication process can also occur spontaneously in response to various environmental stresses, such as UV radiation or certain chemicals. Though continuous, certain conditions like stress or malnutrition can cause it to slow down or stop altogether.
How long does replication take?
The time it takes for DNA replication to occur can vary depending on several factors, including the organism’s specific genome and the ambient temperature. In general, however, the process of DNA replication is relatively rapid. For example, in E. coli, one of the most well-studied organisms, DNA replication typically takes between 20 and 40 minutes to complete. DNA replication is vital in allowing cells to divide and produce new cells rapidly.
Why does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication is essential for cell division and the continuation of life. This is why scientists have worked hard to determine when DNA replication occurs and why it occurs in the first place. When a cell divides, the daughter cells need identical copies of the DNA. This is essential because it allows cells to grow and develop and ensures that genetic information is preserved.