The US space shuttle program was launched in 1981 with the mission of providing safe, reliable, and affordable access to space. The program lasted 39 years and completed 135 missions, traveling over 513.7 million miles in orbit and spending more than 1,323 days outside the Earth’s atmosphere.
So, when was the last space shuttle launch?
Learn in This Article
- When Was the Last Space Shuttle Launch
- Why Was the Space Shuttle Retired
- Where Are the Space Shuttles Now
- Atlantis’s History
- Test Flights
- The Crew of STS-135
- Early Missions
- Last Mission
- Ten-Year Anniversary
- What Is Next
- Orion
- The Space Launch System
- Key Takeaways
List of Space Shuttle Missions
Before we talk about the last space shuttle launch, let’s see just how many missions these shuttles flew in the almost 40 years NASA ran the program.
- Columbia completed its maiden voyage in April 1981 and went on to complete 27 missions before being lost in a tragic accident in February 2003.
- Challenger also completed nine missions before it was lost in an accident in January 1986.
- Discovery flew 39 times, including one of the final missions of the space shuttle program in March 2011.
- Atlantis flew 33 times, including the last mission to repair the Hubble Space Telescope in May 2009. Atlantis was also the last space shuttle of NASA to launch before the program ended in July 2011.
- Endeavour completed 25 missions before being retired in June 2011 (notably marking the first time an African-American woman, Mae C. Jemison, traveled to space).
These spacecraft helped build the International Space Station, repair and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope, deploy satellites, and conduct scientific research that has brought us many insights about our Solar System and beyond. They also inspired a new generation of scientists and engineers and demonstrated the power of human ingenuity and cooperation.
When Was the Last Space Shuttle Launch
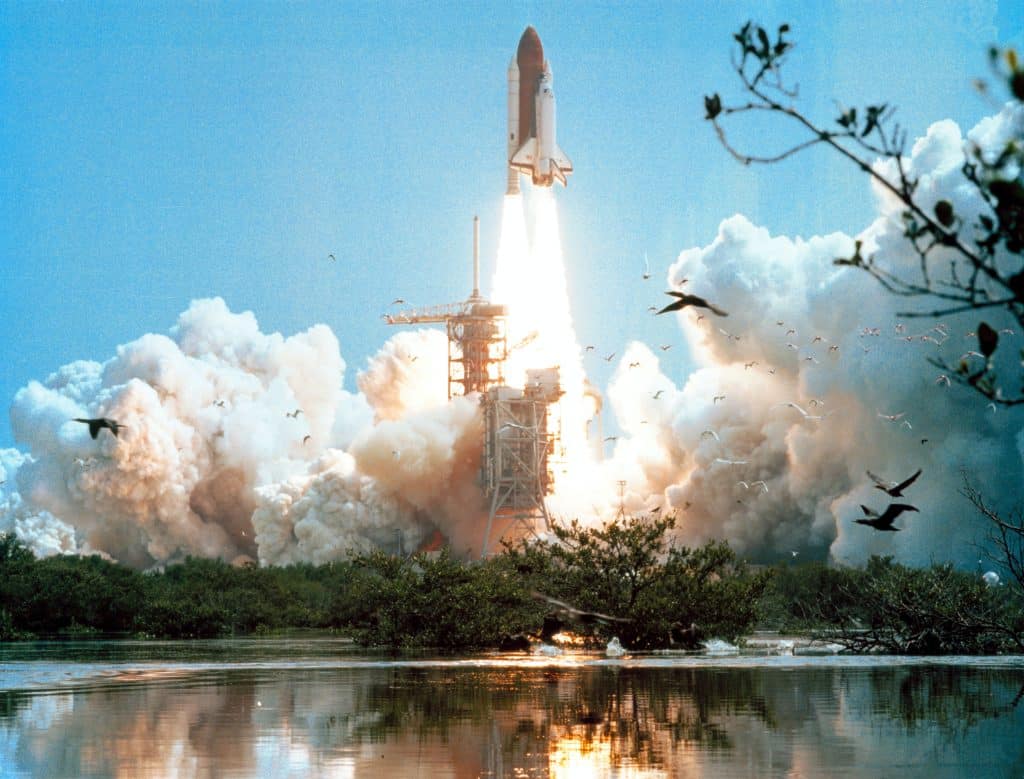
The last space shuttle launch occurred on July 8, 2011, when the shuttle Atlantis took off from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mission, STS-135, was the final flight of the Space Shuttle program, and Atlantis carried a crew of four astronauts and a payload of supplies to the International Space Station.
The last mission was initially scheduled for June 28 but was delayed due to bad weather. After a successful launch and docking with the space station, Atlantis returned to Earth on July 21, 2011. NASA announced that the space shuttle program was ending after 39 years of service, shifting the focus to developing new spacecraft for deep space exploration.

Why Was the Space Shuttle Retired
NASA retired the space shuttle for several reasons, including the high cost of operating the shuttles and the age of the fleet. The last space shuttle was built in 1991, and by the time the program ended, the shuttles were more than 20 years old.
NASA also has a new heavy-lift rocket, the Space Launch System, which is being developed to replace the space shuttle. The Space Launch System can carry larger payloads and will be more powerful than any rocket ever built. NASA is also working on developing new spacecraft for human exploration of deep space.
Where Are the Space Shuttles Now
The formerly active space shuttles, Atlantis, Discovery, Endeavour, and Enterprise are on display at museums across the United States.
- Atlantis is on display in the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida.
- Discovery is on display in the Steven Fudvar-Hazy Center in Virginia.
- Endeavour is on display in the California Science Center in Los Angeles.
- Enterprise is on display in the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York.
These museums offer visitors the opportunity to learn about the history of the space shuttle program and the science and technology that made it possible.
Atlantis’s History
The space shuttle Atlantis was the fourth orbiter of the Space Shuttle program. It first flew in 1985 and completed 33 missions before retiring in 2011. Atlantis is best known for its role in repairing and upgrading the Hubble Space Telescope. The telescope was deployed into orbit by Atlantis in 1990 and underwent a series of repairs and upgrades during subsequent missions.
Atlantis also carried out the final shuttle mission of the program, STS-135, in 2011. The mission delivered supplies to the International Space Station and marked the end of an era for American space exploration.
Test Flights of the Space Shuttle
The first test flight of the space shuttle was STS-1, which launched on April 12, 1981. The mission was piloted by astronauts John Young and Robert Crippen. STS-1 was the first time a spacecraft was launched into space with humans on board since the Apollo program. The mission was also the first time a spacecraft was launched vertically like a rocket and then landed horizontally like an airplane.
The Crew of STS-135
The crew of STS-135 was made up of four astronauts: commander Chris Ferguson, pilot Doug Hurley, and mission specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim. Ferguson and Hurley were veteran astronauts, experienced in flying on the space shuttle, and Magnus and Walheim were experienced spacewalkers. All four astronauts had participated in multiple spaceflight missions before STS-135.
Early Missions of the Space Shuttle Atlantis
Atlantis made its maiden voyage in 1985 on STS-51-J, a classified military mission. The shuttle’s first public mission was STS-61-B in November 1985, when it launched a communications satellite into orbit. In 1990, Atlantis carried the Hubble Space Telescope into orbit and deployed it for the first time. The telescope has been repaired and upgraded on subsequent missions by Atlantis and other space shuttles.
The Final Mission of the Space Shuttle Atlantis
In 2011, the space shuttle Atlantis embarked on the final STS-135 mission, launched on July 8. Atlantis participated in 33 missions. STS-135 delivered supplies to the International Space Station and marked the end of NASA’s space shuttle program.
Ten-Year Anniversary of the Last Space Shuttle Launch
On July 8, 2021, it was ten years since the last space shuttle launch. The space shuttle program ended after the final mission of the space shuttle Atlantis in 2011. Although there are no longer any active space shuttles, their legacy continues to live on through many discoveries and achievements.
The space shuttle program was a remarkable achievement in American space exploration. Over the course of 39 years, the space shuttle fleet completed 135 missions and made countless contributions to science and technology.
What Is Next?
Now that the space shuttle program has ended, what is the next step in American space exploration? What is going to be the space shuttle replacement? The answer is unclear. There are many concepts for future spacecraft but no definite plans. NASA is developing a new heavy-lift rocket called the Space Launch System (SLS).
The SLS will be capable of launching crewed missions to deep-space destinations such as Mars. NASA is also working on a new Orion spacecraft used for deep-space exploration. The
first test flight of the SLS is scheduled for August 2022, and three Orion spacecraft are under construction. These new vehicles will allow us to continue exploring our solar system and beyond.
Orion
Orion is a spacecraft designed for deep-space exploration. NASA is developing the spacecraft as part of the agency’s next generation of space exploration vehicles. Orion will be capable of carrying astronauts to destinations such as Mars and other deep-space destinations.
The Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is a new heavy-lift rocket developed by NASA. The SLS will be the most powerful rocket ever built, and it will be capable of launching crewed missions to deep-space destinations. The first test flight of the SLS is scheduled for August 2022, and the SLS will be an essential part of future American space exploration efforts.
Key Takeaways
Atlantis was launched for the last time on July 8, 2011, and after 39 years of service, the space shuttle program ended. The space shuttles were used for various purposes, from conducting research in orbit to repairing the Hubble Space Telescope to resupplying the astronauts on the ISS. With the end of the space shuttle program, NASA is now looking for new transportation methods to help us explore our universe.
Frequently Asked Questions
July 8, 2011, was the final launch of the space shuttle Atlantis and the last mission of the space shuttle program.
After the final mission was launched, many people asked themselves, is NASA still operating? And the answer is yes, NASA still exists. Although the space shuttle program has ended, NASA continues to work on new spacecraft and rockets to enable future missions.
The space shuttle program ended because it was time to change the way we explore space. The space shuttles were used for various purposes, from conducting research in orbit to repairing the Hubble Space Telescope. With the end of the space shuttle program, NASA is now looking for new transportation methods to help us explore our universe.
It already did; the answer to this question is the same as the answer to when was the last space shuttle launch? On July 8, 2011, the space shuttle Atlantis took off from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The final mission of the space shuttle marked the end of an era for American space exploration.